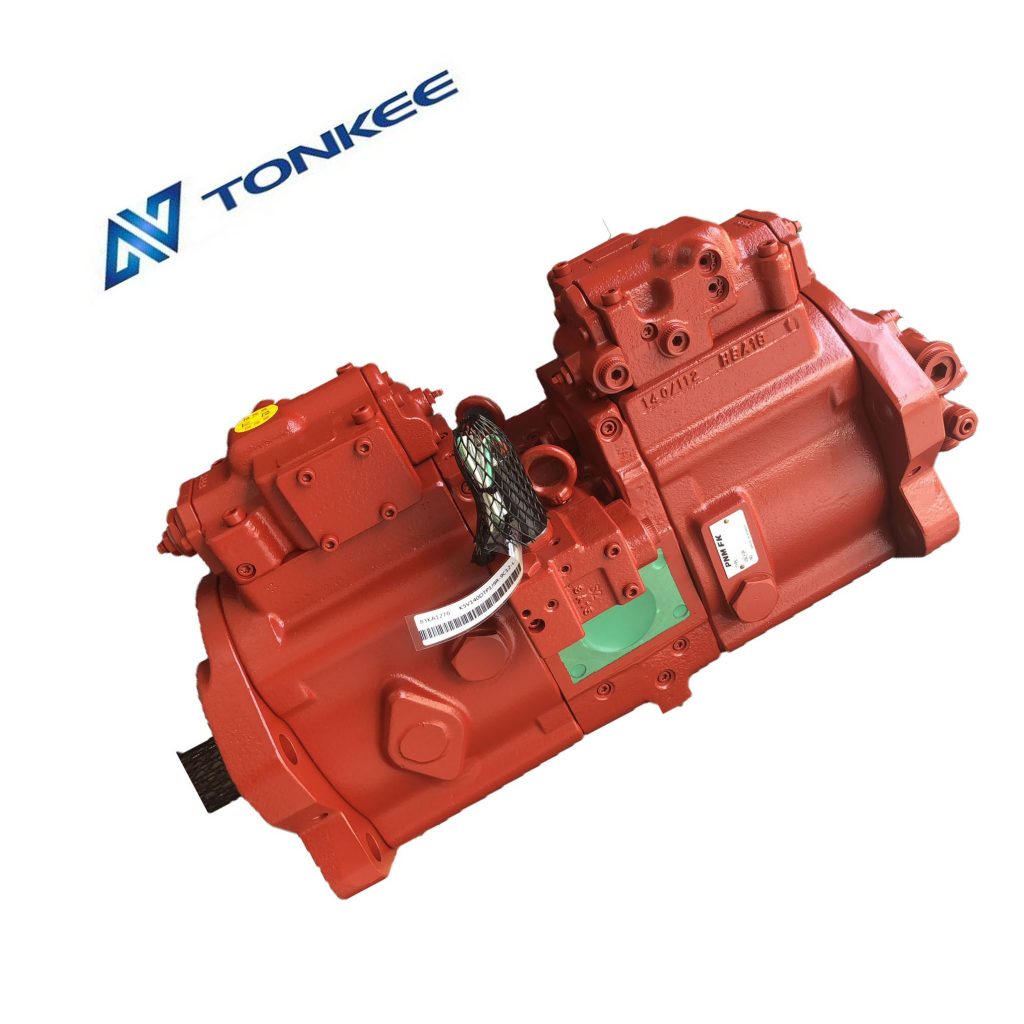
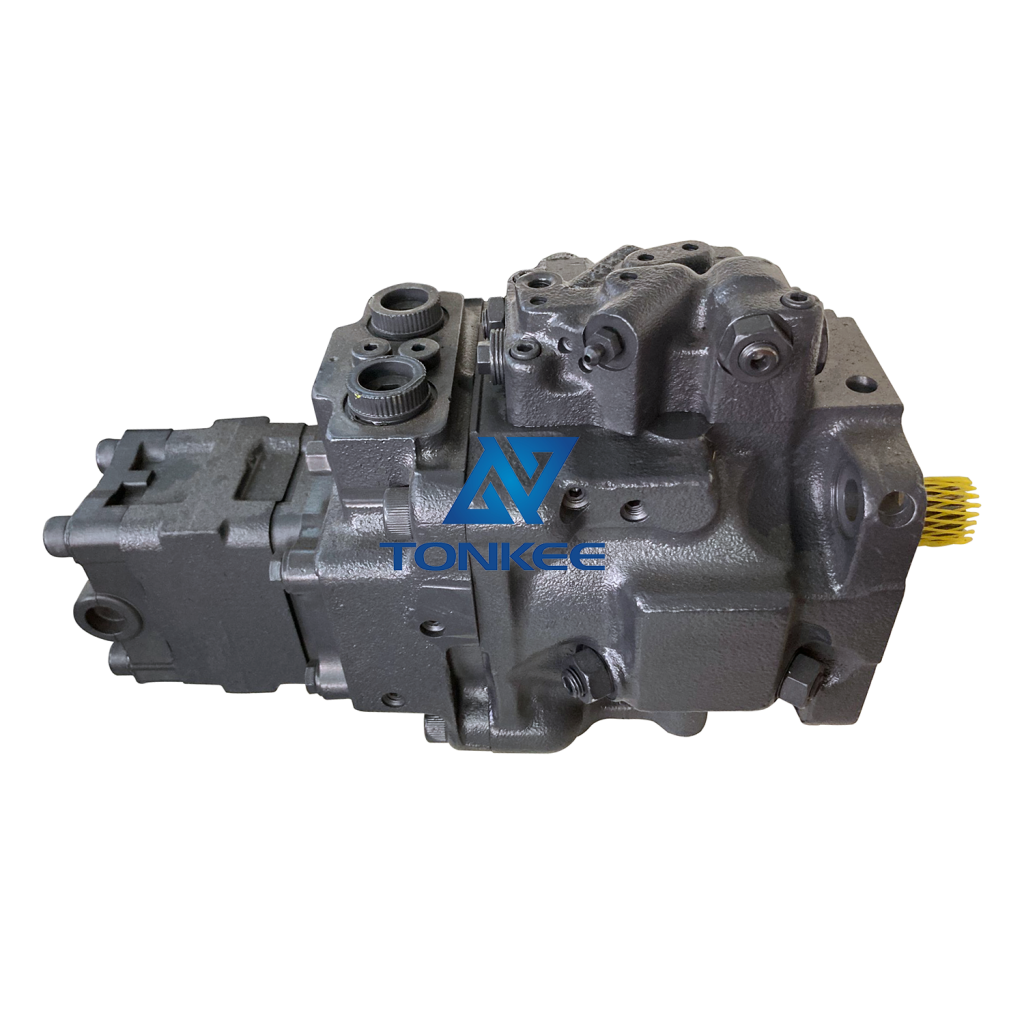
The fuel pump in these engines is responsible for drawing diesel fuel from the fuel tank and delivering it to the engine's injectors.
It ensures that the engine receives a consistent and pressurized supply of fuel, which is essential for efficient combustion and optimal performance. The fuel pump is driven by the engine's camshaft or gear train and operates in sync with the engine's cycles.
Types of Fuel Pumps:
There are primarily two types of fuel pumps used in excavator engines: mechanical and electronic fuel pumps. Mechanical fuel pumps are often driven directly by the engine's camshaft, while electronic fuel pumps are controlled by the engine's electronic control unit (ECU). The choice of fuel pump type depends on the engine model and its specific requirements.
Fuel Pump Specifications:
Fuel pumps in these excavator engines are designed to meet stringent specifications to ensure reliable and efficient operation. Here are some key specifications:
Flow Rate: The fuel pump is designed to deliver a precise amount of fuel per unit of time, typically measured in liters per hour (LPH) or gallons per hour (GPH). The flow rate is carefully calibrated to match the engine's requirements.
Pressure Rating: The fuel pump is responsible for maintaining the required fuel pressure within the fuel injection system.
The pressure rating is specified in pounds per square inch (psi) or bar and is essential for achieving proper atomization of the fuel during combustion.
Materials: Fuel pumps are constructed with high-quality materials to withstand the corrosive nature of diesel fuel and the rigors of engine operation. Components within the pump are often made of durable materials like stainless steel and hardened alloys.
Filtration: Fuel pumps are equipped with built-in filters to ensure that the fuel delivered to the engine is free from contaminants and impurities. Proper filtration is crucial to prevent damage to the fuel injection system.
Seals and Gaskets: Fuel pumps come with high-quality seals and gaskets to prevent fuel leaks and maintain the required pressure in the fuel system. These components are designed to withstand the demanding conditions of the engine environment.
Durability and Reliability: Fuel pumps are built to last, often with features like precision machining and quality control to ensure long-term durability and reliability.
Importance of Fuel Pump Maintenance:
Proper maintenance of the fuel pump is crucial to ensure the engine's longevity and performance. Regular inspections, cleaning of fuel filters, and adherence to recommended service intervals are essential to prevent fuel system issues and breakdowns. Any signs of reduced fuel flow or pressure should be promptly addressed to prevent engine damage.



 English
English Русский язык
Русский язык